Design and development of Co3O4/NiO composite nanofibers for the application of highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensors
Abstract
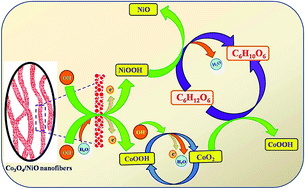
Cobaltosic oxide/nickel oxide (Co3O4/NiO) composite nanofibers were synthesized via an electrospinning technique and their electrocatalytic activities toward non-enzymatic glucose sensors were evaluated in detail. The Co3O4/NiO composite exhibited the homogeneously distributed nanofibers with high porosity, effective inter connectivity and an extended number of conducting channels with an average diameter of 160 nm. The diffraction patterns depicted the face centred cubic crystalline structure of Co3O4/NiO nanofibers and the purity of the composite nanofibers was further ensured by using FT-IR and UV-vis spectroscopic analyses. The electrocatalytic performances of prepared nanofibers toward the oxidation of glucose was determined by cyclic voltammetry and amperometry techniques and the experimental results showed that the Co3O4/NiO composite nanofibers exhibited a maximum electrooxidation toward glucose, owing to the synergistic effect of Co3O4 and NiO. The electrospun Co3O4/NiO nanofibers exhibited a detection limit of 0.17 μM, a wide linear range of 1 μM to 9.055 mM and a high sensitivity of 2477 μA mM−1 cm−2. The nanofibers have also exhibited favorable properties such as good selectivity, reproducibility, durability and real sample analysis, which ensured its potential applications in the clinical diagnosis of diabetes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...