A novel copper(ii) complex with an unsymmetrical tridentate-Schiff base: synthesis, crystal structure, electrochemical, morphological and electrocatalytic behaviors toward electroreduction of alkyl and aryl halides†
Abstract
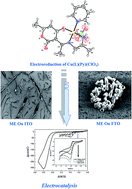
This work describes the synthesis of a new unsymmetrical tetradentate copper(II) Schiff base complex Cu(L)(Py)(ClO4) containing N3O donor atoms. The tridentate ligand (HL) has been prepared by condensation of dehydroacetic acid on 1,2-diaminopropane in methanol. The reaction of the ligand with an appropriate amount of copper(II) perchlorate hexahydrate (1 : 1 ratio) in the same solvent and in the presence of an excess of pyridine (Py) yields the title compound. The tridentate ligand (HL) with pyridine act as mixed ligands where three nitrogen and an enolic oxygen atoms were chelated to the copper centre. This complex has been fully characterized by FT-IR, UV-Vis spectrophotometry, and cyclic voltammetry. Single crystal X-ray diffraction of this complex showed that the copper ion was coordinated by one ligand, one pyridine molecule with one perchlorate anion in a square pyramidal geometry. The Cu(L)(Py)(ClO4) complex crystallizes in an orthorhombic system, space group of ![[P with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0050_0304.gif) cab with a = 11.051, b = 15.58, c = 21.736 Å and Z = 8. The electrochemical reduction of the copper(II) complex, in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent using cyclic voltammetry, produces conducting polymeric films on different electrode substrates, such as glassy carbon (GC), indium tin oxide (ITO) and fluorine tin oxide (FTO). The catalytic activity of this complex in homogeneous and heterogeneous electrocatalytic media seems to be efficient for the electroreduction of bromocyclopentane and iodobenzene.
cab with a = 11.051, b = 15.58, c = 21.736 Å and Z = 8. The electrochemical reduction of the copper(II) complex, in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent using cyclic voltammetry, produces conducting polymeric films on different electrode substrates, such as glassy carbon (GC), indium tin oxide (ITO) and fluorine tin oxide (FTO). The catalytic activity of this complex in homogeneous and heterogeneous electrocatalytic media seems to be efficient for the electroreduction of bromocyclopentane and iodobenzene.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...