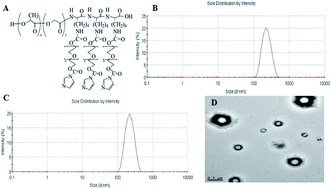
PEG–PLGA–PLL nanoparticles in combination with gambogic acid for reversing multidrug resistance of K562/A02 cells to daunorubicin
Abstract
The present chemotherapy in malignancy treatment, including leukaemia, is plagued by one main problem: multidrug resistance (MDR) which is often related to excessive expression of adenosine triphosphate-dependent efflux pump. In recent years, attempts have been focused on searching competitive inhibitors. However, high toxicity and severe side effects were the main impediments for the application of inhibitors. Therefore, this study investigated a new strategy to utilise polyethylene glycol–polylactic-co-glycolic acid–poly-L-lysine (PEG–PLGA–PLL) as a delivery system to combine with gambogic acid (GA) with the purpose of delivering daunorubicin (DNR) to the target location to reserve MDR with maximised therapeutic efficacy and minimised side effects. The anti-tumour ability of DNR in the presence of GA–PEG–PLGA–PLL was evaluated by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay, flow cytometry and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining. The possible signalling pathway was demonstrated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (QPCR) and Western blot assay. The results showed that the intracellular concentration of DNR can evidently increase with the presence of GA–PEG–PLGA–PLL, and the resistance of K562/A02 cells to DNR can be reversed when combined with GA–PEG–PLGA–PLL, which acted as a delivery system. Thus, anti-tumour efficiency was promoted. Overall, GA–PEG–PLGA–PLL can be a promising agent in reversing MDR of K562/A02 to DNR.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...