Influence of the bimodal pore structure on the CO hydrogenation activity and selectivity of cobalt catalysts
Abstract
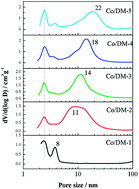
A series of Co-based catalysts supported on different silica-based bimodal mesoporous materials for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTs) were prepared by the incipient wetness impregnation (IWI) method. The results showed that Co-based catalysts presented a bimodal mesoporous structure. Catalysis and characterization results showed that the bimodal structure strongly influenced the dispersion of cobalt species and the F–T catalytic performance. Moreover, the F–T synthesis results showed that the catalysts with a bimodal pore size distribution of 2.5 and 8 nm or 2.5 and 11 nm had a lower methane selectivity than those with larger pores. The catalyst with a 2.5 and 22 nm pore size distribution showed the highest activity and the highest selectivity to C5–11.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...