Molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for atrazine detection by electropolymerization of o-phenylenediamine†
Abstract
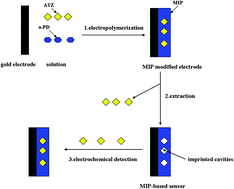
A sensitive and selective atrazine (ATZ) electrochemical sensor was developed based on a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP). Density functional theory at the B3LYP/6-31G (d,p) level and the Gaussian 2009 package was used to calculate the interaction energy of template-monomers. The MIP sensing film was prepared by electropolymerization of o-phenylenediamine (o-PD) using ATZ as the template. Some factors affecting the activity of the sensor have been discussed. The performance of the sensor was characterized by cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry. Under the optimal experimental conditions, the relative current change was linear to the concentration of ATZ in the range of 5.0 × 10−9 to 1.4 × 10−7 M with a detection limit of 1.0 × 10−9 M. The result of the selectivity experiment showed that the imprinted electrode has a good response and selectivity towards ATZ. The proposed MIP-based sensor also showed good stability and repeatability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...