Pretreatment of miscanthus using 1,3-dimethyl-imidazolium methyl phosphonate (DMIMMPh) ionic liquid for glucose recovery and ethanol production†
Abstract
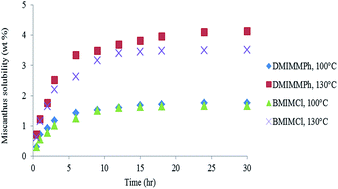
An environmentally friendly method for the extraction of cellulose from miscanthus using 1,3-dimethyl-imidazolium methyl phosphonate (DMIMMPh) ionic liquid is described. The parameters affecting the extraction process are temperature and time. Extraction results were evaluated using a Box–Behnken Design. The pretreatment of miscanthus with ionic liquids resulted in the regeneration of amorphous, porous cellulose almost free of lignin, which is suitable for enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation processes. The regenerated cellulose can be hydrolyzed efficiently into glucose using cellulase enzyme with glucose hydrolysis efficiency exceeding 93%. The hydrolysate is converted into ethanol with fermentation using Saccharomyces cerevisaie yeast with an ethanol conversion rate reaching up to 85%. A successful ethanol production was obtained with an overall ethanol yield reaching up to 148 g ethanol kg−1 miscanthus. This indicates the high performance of DMIMMPh ionic liquid in converting biomass feedstocks into ethanol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...