Effect of heat treatment on the lubricating properties of lithium lubricating grease
Abstract
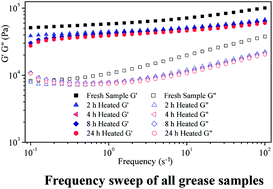
Owing to the potential oxidation and thermal degradation of lithium lubricating grease when the grease is heated to improve its fluidity in the pumping process, fresh NLGI 3 lithium lubricating grease samples were heated to obtain experimental samples to simulate the static thermal degradation by using a drying oven. The microstructure and infrared spectra were studied by using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) techniques respectively. The rheological properties were estimated by a rotational rheometer and the tribological properties were evaluated on a four-ball testing machine. Finally, the action mechanisms of the effect of heat treatment on the tribological properties of lithium lubricating grease are discussed. The experimental results showed that the lithium lubricating grease samples exhibited better antifriction and antiwear properties after heat treatment at 120 °C, which is not obvious during 0–4 h, while the coefficient friction and extreme pressure progressively decreased during 4–24 h. Meanwhile, oxidative and thermal degradation do not proceed after heat treatment for 0–24 h according to the FESEM and FTIR results. Finally, it was confirmed that the variation of physical entanglement, which was caused by a short heat treatment, would vary the tribological properties of the lithium lubricating grease.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...