Hydroxycinnamic acid as a novel scaffold for the development of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors
Abstract
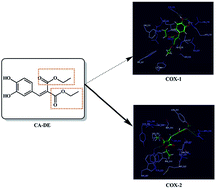
Cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes are involved in inflammation and cancer. Nine derivatives of hydroxycinnamic acid including ethyl and diethyl esters were synthesized and tested as COX inhibitors in a whole blood assay. Esterification improved COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitory activities of the derivatives. Ethyl esters were more effective against COX-1 and the most potent one was caffeic acid ethyl ester. Interestingly, diethyl esters showed selectivity towards COX-2; the most active compound was caffeic acid diethyl ester (CA-DE) with 88.5 and 30.5% inhibition against COX-2 at 100 and 20 μM, respectively, while it was almost inactive against COX-1. Docking studies showed that CA-DE forms 3 hydrogen bonds with the active site of COX-2 (4-OH⋯OH-Tyr355, 4-OH⋯NH-Arg120 and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯OH-Tyr385), while it forms only the first two bonds with COX-1. Furthermore, the Val523 residue in COX-2 provides a wide hydrophobic pocket, which would accommodate diethyl esters. The present approach inspired by a natural scaffold provides an asset for the generation of new chemical entities endowed with selective COX-2 inhibitory activity.
O⋯OH-Tyr385), while it forms only the first two bonds with COX-1. Furthermore, the Val523 residue in COX-2 provides a wide hydrophobic pocket, which would accommodate diethyl esters. The present approach inspired by a natural scaffold provides an asset for the generation of new chemical entities endowed with selective COX-2 inhibitory activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...