Molecular weight dependence of structure and properties of chitosan oligomers†
Abstract
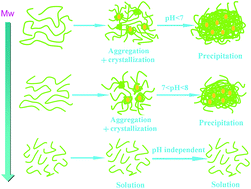
In this work, chitosan oligomers (COS) with molecular weights decreasing continuously and covering the region of insoluble–soluble transition and with low polydispersity were prepared, and then the molecular weight (MW) dependence on the structure and properties were studied. FTIR, 1H and 13C NMR analyses showed that the prepared COS maintained the chemical structure of the initial chitosan and some signal shifts were observed resulting from the increase of the degree of acetylation. In contrast, it was found that the crystalline structure, thermal stability, and water solubility were significantly influenced by the MW, that is, with the decrease of the MW, the crystalline structure transformed from “L-2” to “tendon” and then to “annealed” polymorph, in which the MW corresponding to the conversion from “tendon” to “annealed” polymorph was 4.67 kDa. The thermal stability decreased with the reduction of the MW, while for the similar MW, the stability increased with the increase of the crystallinity. For water solubility, the MW ranging from 3.82 to 4.67 × 103 kDa corresponded to the insoluble–soluble transition. A mechanism of water solubility dependence on MW was proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...