Chitosan coated alginate micro particles for the oral delivery of antifilarial drugs and combinations for intervention in Brugia malayi induced lymphatic filariasis†
Abstract
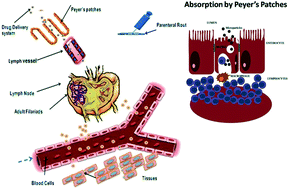
In the present study chitosan (Chi) coated alginate micro particles (MPs) were prepared by a spray drying technique for the effective delivery to lymphatics via combination therapy. The optimized MPs were spherical of less than 5 μm in size with loading and entrapment efficiencies of 14.13 ± 1.1% and 41.28 ± 1.5% for diethylcarbamazine (DEC), and 14.93 ± 0.58% and 43.51 ± 1.9% for doxycycline (DOX) respectively. The physical mixture and drug entrapped MPs showed good stability and no interaction was evident from FT-IR, XRD and thermal analysis. In vitro release studies revealed that the drug release pattern was sustained beyond 16 h in simulated gastro-intestinal fluids for DEC and DOX from the MPs. In vivo ileal uptake and histopathological studies in rats divulged the uptake of the MPs by intestinal epithelium. Further in vitro antifilarial activity studies demonstrated notable killing by the combination therapy compared to individual treatments with Chi–DOX MPs and Chi–DEC MPs. A combined dose of 25 mg kg−1 and 10 mg kg−1 in a 2.5 : 1 ratio of DEC and DOX respectively, following the oral MP therapy, significantly improved the microfilaricidal and macrofilaricidal action of the in vitro estimations. In vivo experiments of infected jirds (Meriones unguiculatus) were carried out. The macrofilaricidal/adulticidal action was enhanced by 2 fold with Chi–DOX MPs in combination with Chi–DEC MPs, microfilaricidal enhancements of the Chi–DEC & Chi–DOX combination are also inferred.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...