Esterification of glycerol over a solid acid biochar catalyst derived from waste biomass
Abstract
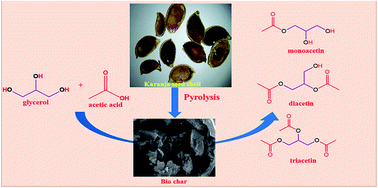
Karanja seed shells were subjected to pyrolysis in an inert atmosphere at different temperatures to prepare a biochar. The biochar was characterized by X-ray diffraction, FT-infrared spectroscopy, laser Raman spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, CHNS-elemental analysis, BET surface area analysis and for the temperature programmed desorption of ammonia. These biochar carbon catalysts were used as catalysts without any functionalization/treatment for the esterification of glycerol with acetic acid. Carbonization at 400 °C led to the formation of biochar with a greater number of strong acidic sites. Amorphous carbon obtained by high temperature carbonization was composed of aromatic carbon sheets oriented in a considerably random fashion. The biochar obtained at 400 °C exhibited the highest glycerol esterification activity. The catalytic activity of the biochar was explained based on its properties derived from the different characterization methods. The biochar catalyst can be reused with consistent activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...