Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of a floating photocatalyst based on B–N-codoped TiO2 grafted on expanded perlite
Abstract
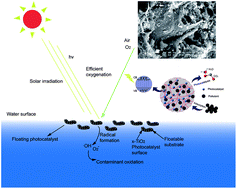
Floating photocatalysts of boron–nitrogen codoped TiO2 grafted on expanded perlite (B–N-TiO2/EP) were prepared by a facile sol–gel method. The catalysts were characterized by thermogravimetric differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption–desorption (BET), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis-DRS). The results showed that by modifying the boron doping content in B–N-TiO2/EP, we could effectively obtain photocatalysts with a high BET surface area and porosity. Increasing the boron doping contents would inhibit the transformation of anatase TiO2 to the rutile phase. Compared with N-TiO2/EP, B–N-TiO2/EP exhibits an evident red-shift of the absorption band edge and the absorption intensity of the visible region increases obviously. The enhanced RhB photodegradation rate of B0.57–N-TiO2/EP could reach 94% after 3 h of visible light irradiation. Moreover, the floating photocatalyst could be easily separated and reused, showing great potential for practical applications in environmental cleanup and solar energy conversion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...