Parameter optimization for nitrate removal from water using activated carbon and composite of activated carbon and Fe2O3 nanoparticles
Abstract
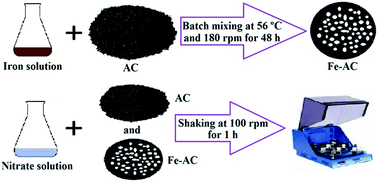
Due to the high solubility of nitrate in water, it is the most widespread contaminant in drinking water sources. In this study, activated carbon (AC) and a composite of activated carbon and Fe2O3 nanoparticles (Fe–AC) were used for nitrate removal from water. AC and Fe–AC adsorbents were characterized using BET, SEM, FTIR and XRF analysis. The main operating parameters such as initial concentration (C0), adsorbent dosage and pH have been optimized for maximum nitrate removal. Experimental design was carried out using Central Composite Design (CCD) with response surface methodology (RSM). Based on RSM analysis, the nitrate removal models proved to be highly significant with very low probability values (<0.0001). From the predicted models, maximum nitrate removal percentages by AC and Fe–AC were 68.45% and 95.56%, respectively. The optimum conditions for AC and Fe–AC were 0.53 g/50 mL adsorbent dosage, pH = 3, C0 = 147.31 mg L−1 and 0.53 g/50 mL, pH = 5.1, C0 = 69.16 mg L−1, respectively. Model predictions fitted the obtained experimental results with relative errors of 6.94% and 4.44% for AC and Fe–AC, respectively. Equilibrium isotherms were analyzed using different models and data were fitted to the Langmuir isotherm. Analysis of kinetic data indicated that data followed a second-order-rate model. The experimental results proved that Fe–AC as new adsorbent promotes the percentage of nitrate removal significantly.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...