Organotin carboxylate catalyst in urethane formation in a polar solvent: an experimental and computational study†
Abstract
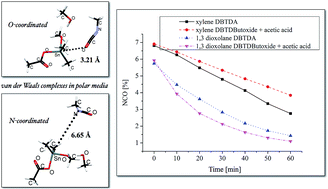
Organotin carboxylates are important catalysts in aliphatic urethane synthesis. They are widely used in two component urethane systems such as casting systems, high performance coatings and in the synthesis of one-component moisture cure urethane pre-polymers for coatings. In most of these systems, a solvent is used to reduce the viscosity to assist application. In general, aromatic hydrocarbon solvents such as xylene, R100 or oxygenated solvents (e.g. esters) are used. In this paper, a detailed investigation of the catalytic mechanism of organotin carboxylate in urethane synthesis in a polar medium is investigated using experimental and computational methods. There is evidence that the dominant catalyst for organotin carboxylate catalysis of aliphatic isocyanate in urethane formation in a polar medium is organotin alkoxide. In this work, DFT studies on B3LYP/LANL2DZ/6-31+G** level of theory with the CPCM solvent model was used to study the reactivity between isocyanate and alcohol in the presence of a selected organotin catalyst in different mediums. The theoretical studies were supported by experimental evidence.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...