Mesocarbon microsphere composites with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness
Abstract
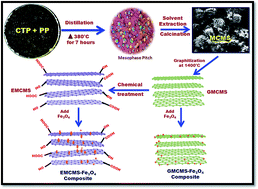
Development of advanced carbon based materials with improved microstructure properties, finding widespread applications in electromagnetic shielding is a challenge for the scientific community. This research paper describes a method, which is simple and economic for the synthesis of mesocarbon microspheres (MCMS) from heat treatment of coal tar pitch and petroleum pitch followed by solvent extraction. The MCMS were then semi-graphitized (GMCMS) at 1400 °C and the distance between the graphitic layers of GMCMS was increased by a chemical treatment called expanded EMCMS. Further, Fe3O4 nanoparticles were in situ incorporated in GMCMS and EMCMS. All the samples were characterized for various parameters, particularly with regard to their potential use in electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness in the X-band of the frequency range of 8.2 GHz to 12.4 GHz. A maximum total shielding effectiveness (SET) of −65.4 and −75.8 dB for GMCMS–Fe3O4 and EMCMS–Fe3O4, respectively was achieved which is more than double for the bare samples, i.e., −29 and −32 dB for GMCMS and EMCMS, respectively. A total SET was obtained for the EMCMS–Fe3O4 composite of ∼−75.8 dB in the whole X band which is remarkably high compared to other reported values in the literature. EM parameters such as relative complex permittivity and relative complex permeability of all the composites were also studied in the X band frequency range.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...