Cadmium selenide quantum dots solar cells featuring nickel sulfide/polyaniline as efficient counter electrode provide 4.15% efficiency
Abstract
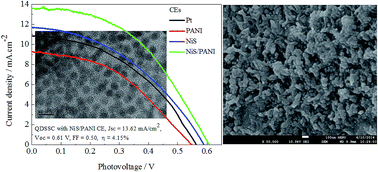
Nickel sulfide decorated polyaniline (NiS/PANI) co-deposition onto fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) substrate using an in situ electropolymerization route and served as the counter electrode (CE) for polysulfide electrolyte in cadmium selenide (CdSe) quantum dots sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs). The NiS/PANI CE provided great electrocatalytic activity and lower charge-transfer resistance compared to the platinum (Pt), NiS and PANI CEs under the same preparation conditions prepared using cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and Tafel polarization plots characterization. It was because the photoanode was modified with a TiO2 dense layer and thioglycolic acid that the QDSSC exhibited an improved fill factor and short-circuit current density. Under optimum conditions, the QDSSC featuring a NiS/PANI counter electrode provided an enhanced power conversion efficiency of 4.15% under an illumination of 100 mW cm−2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...