Development and validation of a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for determination of sterol oxidation products in edible oils†
Abstract
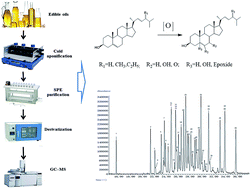
An efficient gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method was developed and validated for determination of sterol oxidation products (SOPs) in edible oils. The sample preparation involved cold saponification, liquid–liquid extraction, solid-phase extraction on a silica gel cartridge, and trimethylsilylation by N-methyl-N-(trimethylsilyl) heptafluorobutyramide with 5% 1-methyl imidazole. The trimethylsilyl ether derivatives of SOPs were separated by gas chromatography with a 30 m DB-5MS capillary column and quantified by a mass spectrometer in selective ion monitoring mode. 5α-Cholestane and 19-hydroxycholesterol were used as dual internal standards. The calibration curves for each compound showed correlation coefficients (R2) better than 0.98. The detection limits were below 12.9 ng mL−1 (except for epoxides). The intra- and inter-day determination precisions for diversiform SOPs were <10% in relative standard deviations; the recoveries ranged within 89.72% and 117.42%. The developed approach was successfully applied to study the presence of thirty-four different SOPs present at low levels in camellia, olive, sesame, peanut, rapeseed, rice bran, soybean and corn oils.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...