Core–shell structured MgO@mesoporous silica spheres for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue and lead ions†
Abstract
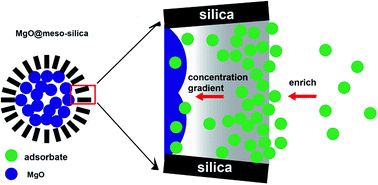
Core–shell structured MgO@mesoporous silica spheres are synthesized by a two-step programmed method. MgO@mesoporous silica exhibits a high BET specific surface area of 567 m2 g−1 and a pore volume of 1.08 cm3 g−1. The stable mesoporous silica coating not only serves as a strong shell to improve the mechanical stability of MgO, but also enriches the adsorbates in the mesopores to reach a higher adsorption rate. The core–shell MgO@mesoporous silica spheres exhibit excellent removal capabilities of 3297 mg g−1 for Pb2+ and 420 mg g−1 for methylene blue, which are much higher than those of MgO itself.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...