Computational investigation of the ligand field effect to improve the photoacoustic properties of organometallic carbonyl clusters
Abstract
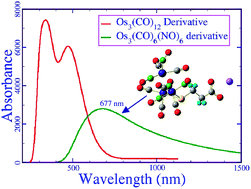
Water soluble organometallic carbonyl clusters are biocompatible, stable and reliable high-contrast photoacoustic contrast agents (PACAs). However, they have limited applications and efficacy due to their absorption in the visible region, which consists of wavelengths that have poor penetration depth inside tissue. In this article, we present the molecular level understanding of these compounds and investigate an alternative way to improve their photoacoustic properties. We discovered that organometallic nitrosyl carbonyl compounds, such as [Os3(CO)6(NO)4(μ-NO)(μ-S(CH2)2COO)]−Na+, which shows high absorption in the near infrared region (λmax = 755 nm), are more suitable photoacoustic contrast agents than other carbonyl clusters that have been reported in the literature to date. As the metal nitrosyl bond is easily oxidisable, these compounds may also be used to study the reactive oxygen species in a living cell. We introduce a theoretical model to calculate the relative toxicity of a compound in terms of electric dipole moment (μ) and reactivity index (ω). Therefore, we computed the μ and ω values for all of the clusters. It was shown that the modeled nitrosyl carbonyl compound is much less toxic than the reported carbonyl clusters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...