Nb and Zr modified MWW zeolites – characterisation and catalytic activity
Abstract
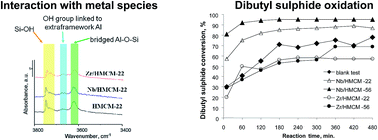
Hydrogen forms of MCM-22 and delaminated MCM-56 zeolites were modified with niobium and zirconium species. The structure/texture and surface properties, as well as the catalytic activity for dibutyl sulfide oxidation, of the two types of modified zeolites were compared. The presence of Brønsted (BAS) and Lewis (LAS) acid sites was detected after pyridine adsorption in all the prepared materials. The highest number of BAS and LAS was observed for HMCM-22. The number of BAS significantly decreased after metal modification because of the interaction between the metal sources and the BAS. External silanol groups of zeolites also participate in metal anchoring. The catalysts obtained were tested for liquid phase dibutyl sulfide oxidation with hydrogen peroxide. The texture of the zeolites and the nature of the metal modifier have a crucial effect on the oxidation of dibutyl sulfide. MCM-56 zeolites are more active than their counterparts of MCM-22 type. Application of niobium containing zeolites significantly increases the reaction rate, leading to 95% conversion after 3 h. The remarkable role of the Nb species is due to its interaction with H2O2 towards peroxo/superoxo species. Modification of both zeolites with zirconium does not increase their activity because of the strong interaction of zirconium species with sulfur compounds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...