Synthesis and properties of a bio-based epoxy resin from 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA)
Abstract
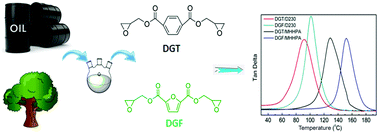
A bio-based epoxy monomer, diglycidyl ester of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (DGF) was synthesized for the first time from the renewable 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). For comparison study, its petroleum-based counterpart, diglycidyl ester of terephthalic acid (DGT) was also prepared. Their chemical structures were confirmed in detail by 1H NMR, 13C NMR and FT-IR before they were cured by methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride (MHHPA) and poly(propylene glycol)bis(2-aminopropyl ether) (D230), respectively. The curing behaviors were investigated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The thermal mechanical properties and thermal stabilities of the cured resins were evaluated using dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Results showed that DGF displayed higher curing activity, elevated glass transition temperature and similar mechanical properties compared with those of the cured DGT. This study indicated that FDCA had a huge potential to replace the petroleum-based terephthalic acid in the synthesis of epoxy resins with satisfactory performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...