Exploring the effect of manganese in lead sulfide quantum dot sensitized solar cell to enhance the photovoltaic performance†
Abstract
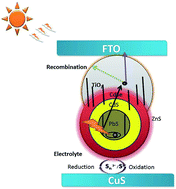
Herein we demonstrate for the first time, the combination of PbS with CdSe/CdS/TiO2 and exploring the impact of manganese (Mn) on PbS (lead sulfide) quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs). Photo-anodes were sensitized with different percentages of Mn content (5, 10 and 15%) on PbS/CdS/CdSe using a simple successive ion layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) technique. The performance of the QDSSCs is examined in detail using polysulfide electrolyte and a copper sulfide (CuS) counter electrode. The optimized percentage of Mn content on PbS/CdS/CdSe electrode results in higher efficiency compared to bare PbS/CdS/CdSe-sensitized QDs. This is confirmed with photovoltaic studies and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The 10% Mn-doped PbS/CdS/CdSe electrode exhibits short circuit current density of 17.34 mA cm2 with an enhanced power to conversion efficiency (η) of 4.25% under 1 sun illumination (AM 1.5 G, 100 mW cm−2).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...