Electrochemistry of Zn and co-reduction of Zn and Sm from LiCl–KCl melt
Abstract
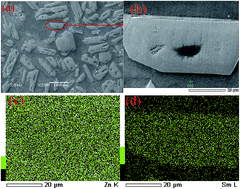
The electrochemical behavior of Zn(II) ions in LiCl–KCl and Sm(III) ions in LiCl–KCl–ZnCl2 melts on a Mo electrode at 773 K was studied by various electrochemical techniques. The results showed that the reduction of Zn(II) to Zn(0) consisted of a one-step process. The electrode reaction of LiCl–KCl–ZnCl2 solutions indicated that the under potential deposition of Sm on pre-deposited Zn electrode formed three kinds of Zn–Sm intermetallic compounds at electrode potentials around −1.57, −2.17 and −2.29 V. The electrochemical extraction of samarium was carried out in LiCl–KCl–ZnCl2 melts on a Mo electrode at 773 K by potentiostatic electrolysis (−2.3 V) for 40 h with an extraction efficiency of 99.87%. Zn–Sm bulk alloy was obtained by galvanostatic electrolysis. The microstructure and micro-zone chemical analysis of the Zn–Sm alloy were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...