Silver nanoparticle-coated “cyborg” microorganisms: rapid assembly of polymer-stabilised nanoparticles on microbial cells†
Abstract
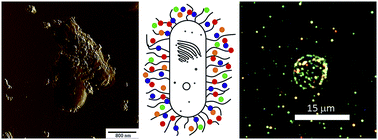
Fabrication of “cyborg” cells (biological cells with surfaces functionalised using a variety of nanomaterials) has become a fascinating area in cell surface engineering. Here we report a simple procedure for fabrication of polycation-stabilised 50 nm silver nanoparticles and application of these nanoparticles for fabrication of viable “cyborg” microbial cells (yeast and bacteria). Cationic polymer-stabilised nanoparticles electrostatically adhere to microbial cells producing an even monolayer on the cell walls, as demonstrated using enhanced dark-field microscopy, atomic force microscopy and microelectrophoresis. Our procedure is exceptionally fast, being completed within 20 min after introduction of cells into nanoparticle aqueous suspensions. Polymer-stabilised silver nanoparticles are highly biocompatible, with viability rates reaching 97%. We utilised “cyborg” cells built using bacteria and silver nanoparticles to deliver nanoparticles into C. elegans microworms. We believe that the technique described here will find numerous applications in cell surface engineering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...