Innovative human-specific investigational approaches to autoimmune disease
Abstract
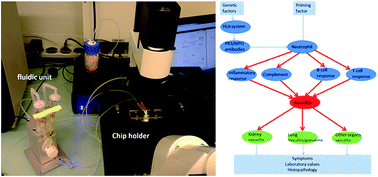
Autoimmune diseases are exclusively human diseases with a complex genetic background and variable clinical presentation, of which the underlying pathophysiology is insufficiently understood. Current treatment is mainly empirical with limited efficacy and significant side effects. To develop more effective targeted therapy for personalized treatment, understanding of the human pathophysiology is crucial, implying a high need for human investigational disease models. Using the example of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) autoimmune vasculitis, the concept of building an in vitro organ-on-chip type human disease model, consisting of cultured organ-specific vascular tissue in interaction with relevant immune system components (e.g. lymph node and thymus tissue) is presented. This in vitro approach makes use of advances in engineering and human stem cell technologies, enabling derivation of pluripotent stem cell lines from patients, differentiation to required cell types, and incorporation in microfluidic chip-based culture systems to optimally mimic in vivo disease conditions. Knowledge-based computational disease modeling is introduced as a valuable complementary tool to generate an integral mechanistic picture of the disease. Combining these multidisciplinary developments promises breakthroughs in understanding autoimmune disease and targeted drug development, while simultaneously reducing use of animal models. Current state of the art and issues remaining to be solved are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...