1,3:2,4-di-(3,4-dimethyl)benzylidene sorbitol organogels used as phase change materials: solvent effects on structure, leakage and thermal performance†
Abstract
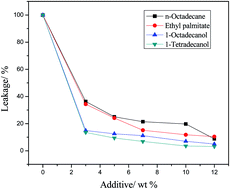
Organogels used as shape-stable phase change materials were prepared by impregnating a low molecular mass organogelator into organic phase change materials. 1,3:2,4-di-(3,4-dimethyl)benzylidene sorbitol (DMDBS) was used as the supporting material and n-octadecane, ethyl palmitate, 1-octadecanol and 1-tetradecanol were used as the phase change materials. The thermal properties, such as phase change temperature and latent heat, were investigated using a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). The leakage and thermal storage performance of the composite phase change materials were also investigated in detail. Rheology measurements were used to demonstrate the true gel phase of the composite phase change materials. Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) were used to determine the chemical structure and microstructure of the composites. The DSC results indicated that the composites exhibited acceptable thermal properties with a high mass percentage of the phase change material. Flory–Huggins parameters (χ) were calculated to estimate the interactions between the gelator and phase change materials. The results indicated that different χ resulted in different morphologies of DMDBS, which led to different leakages and thermal storage performances of the prepared composites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...