Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activities of N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-thiazolidine carboxylic acid†
Abstract
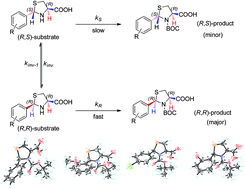
A possible mechanism of dynamic kinetic resolution by the formation of N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-thiazolidine carboxylic acid was proposed and validated by a quantitative density functional theoretical calculation according to Curtin–Hammett principle. Such a mechanism of action of a nucleophilic substitution reaction through an intramolecular hydrogen bonding could be widely applied in the organic syntheses of particular enantiomer. Antibacterial activities showed that most of the N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-(2R)-arylthiazolidine-(4R)-carboxylic acid derivatives exhibited better antibacterial activities against the four bacterial strains than related (2RS)-arylthiazolidine-(4R)-carboxylic acid derivatives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...