Photocatalytic organic degradation over W-rich and Cu-rich CuWO4 under UV and visible light†
Abstract
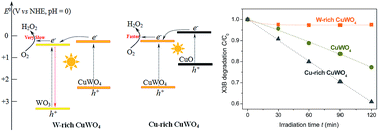
A hydrothermal reaction between Cu(NO3)2 and Na2WO4 at 170 °C, followed by sintering at 500 °C, resulted in the formation of stoichiometric CuWO4 at pH 5.2, while the reactions below and above pH 5.2 gave a mixture of CuWO4 with WO3 and CuO, respectively. For organic degradation in water under visible light, W-rich and Cu-rich samples were less and more active than CuWO4, respectively. A maximum activity was observed with the sample prepared at pH 8.5. Furthermore, this Cu-rich sample shown an activity greatly changing with its sintering temperature, and reaching a maximum at 600 °C. A possible mechanism responsible for the observed activity difference among the samples is proposed, involving the interfacial charge transfer between CuWO4 and WO3 or CuO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...