CoFe2O4@MnFe2O4/polypyrrole nanocomposites for in vitro photothermal/magnetothermal combined therapy†
Abstract
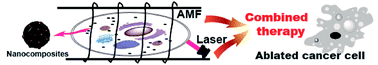
CoFe2O4@MnFe2O4/polypyrrole nanocomposites, in which CoFe2O4@MnFe2O4 core/shell nanoparticles (NPs) were well-distributed in/on polypyrrole (PPy) nanoparticles, have been prepared by the polymerization of pyrrole by Fe3+ in the presence of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and CoFe2O4@MnFe2O4 NPs. In CoFe2O4@MnFe2O4/polypyrrole nanocomposites, the PPy with strong near-infrared absorption can convert 808 nm laser irradiation to heat with a photothermal conversion efficiency of ∼38%, and the CoFe2O4@MnFe2O4 NPs can convert the electromagnetic energy to heat simultaneously in an alternating magnetic field (200 kHz, 60.6 kA m−1) with a specific loss power of 930 W g−1. In vitro experiments showed that the cell viability of 4T1 cells incubated with 200 μg mL−1 of nanocomposites was ∼58% when irradiated by an 808 nm laser (0.2 W cm−2) for 10 min, and ∼68% in an alternating magnetic field (200 kHz, 60.6 kA m−1) for 0.5 h. A combination of 808 nm laser irradiation and alternating magnetic field can ablate nearly all the cells, which suggests the synergistic effect of photothermal and magnetothermal combined therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...