Micropatterned model membrane with quantitatively controlled separation of lipid phases†
Abstract
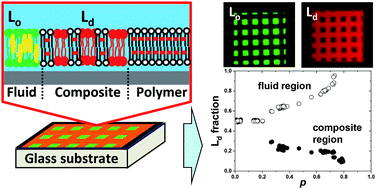
The localization of lipids and proteins in microdomains (lipid rafts) is believed to play important functional roles in the biological membrane. Herein, we report on a micropatterned model membrane that mimics lipid rafts by quantitatively controlling the spatial distribution of lipid phases. We generated a composite membrane of polymeric and fluid lipid bilayers by lithographic polymerization of diacetylene phospholipid(1,2-bis(10,12-tricosadiynoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine: DiynePC). The composite membrane comprised polymer free-region (R0), partially polymerized region (R1), and fully polymerized region (R2). As a ternary mixture of saturated lipid, unsaturated lipid, and cholesterol was introduced into the voids between polymeric bilayers, liquid-ordered (Lo) and liquid-disordered (Ld) lipid phases were accumulated in R0 and R1, respectively. Local enrichment of Ld phase in R1 (and Lo phase in R0) was enhanced with a heightened coverage of polymeric bilayer in R1, supporting the premise that polymeric bilayer domains are inducing the phase separation. The pattern geometry (the area fractions of R0 and R1) also affected the enrichment due to the balance of gross Lo/Ld area fractions. Therefore, we could control the local Lo/Ld ratios by modulating the pattern geometry and polymer coverage in R1. Micropatterned model membrane with quantitatively controlled distribution of Lo/Ld phases offers a new tool to study the functional roles of lipid rafts by enabling to separate membrane-bound molecules according to their affinities to Lo and Ld phases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...