Arsenate removal from aqueous solutions using magnetic mesoporous iron manganese bimetal oxides†
Abstract
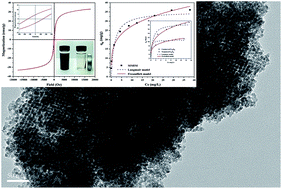
Magnetic mesoporous iron manganese bimetal oxide (MMIM) with high specific surface area, pore volume and well interconnected mesopores was synthesized via the nanocasting strategy using KIT-6 as a hard template. The morphology and physicochemical properties of the samples were characterized using SEM-EDS, TEM, XRD, VSM, FT-IR and XPS, etc. The obtained MMIM was used as an adsorbent to remove arsenate from aqueous solutions, and presented excellent performances for As(V) removal. The adsorption equilibrium data were well described by the Freundlich model, and solution pH values affected the removal efficiency of arsenate significantly, which was due to the isoelectric point (IEP) of the MMIM. The adsorption kinetics fitted a pseudo-second order model, and intra-particle diffusion was not the only rate-limiting step. In addition, MMIM exhibited a sensitive magnetic response and could be easily separated and recovered from aqueous solutions with an external magnetic field. Based on analysis results, possible mechanisms were discussed based on a combination of the results to different theoretical adsorption models.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...