Nickel-catalyzed reductive coupling of alkyl halides with other electrophiles: concept and mechanistic considerations
Abstract
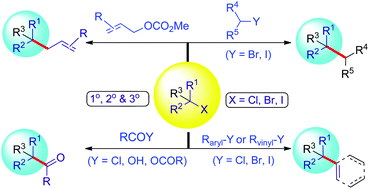
The formation of C–C bonds directly by catalytic reductive cross-coupling of two different electrophiles represents one of the practical synthetic protocols that differs from the conventional nucleophile/electrophile coupling methods. Particularly the reductive coupling of alkyl electrophiles with other electrophiles is still a challenge. This report summarizes the advances in the formation of C(sp3)–C(sp3) bonds between two alkyl electrophiles, with emphasis on the control of chemoselectivity that is exceedingly challenging to achieve due to similar structures and reactivities of two unactivated alkyl halides. The coupling of alkyl halides with aryl or acyl electrophiles was also discussed based on the chemical approach developed by our group, followed by a brief overview of the reactions of tertiary alkyl halides. In the end, a brief overview of the challenges in this exciting field was illustrated. Whereas the reaction mechanisms generating alkyl–alkyl products are proposed to involve reactions of Ni(I) species with alkyl halides to generate Ralkyl–Ni(III)–Ralkyl intermediates through a radical/Ni cage-rebound process, the obtained evidence seemingly supports that the radical chain mechanism governs the acylation and arylation of alkyl halides. The latter features a cage-escaped alkyl radical.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...