Synthesis, structure, and magnetic properties of dicopper and tricobalt complexes based on N-(2-pyridylmethyl)iminodiethanol†
Abstract
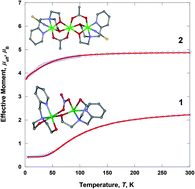
Dinuclear [Cu(H2pmide)(NO3)Cu(Hpmide)](NO3)2 (1) and trinuclear [(pmide)2Co3(CH3CO2)2(NCS)2]·4CH3OH (2) coordination complexes have been prepared by the reaction of the tetradentate H2pmide ligand and Cu(NO3)2·3H2O or Co(CH3CO2)2·4H2O/NaNCS in organic solvent (H2pmide = N-(2-pyridylmethyl)iminodiethanol). In 1, one copper(II) ion is bonded with a H2pmide, and the other is coordinated with a mono-deprotonated Hpmide−. The copper(II) ions are linked through an ethoxo group of the Hpmide− ligand and two oxygen atoms of a nitrate ion, resulting in an asymmetric dinuclear structure. In 2, two terminal cobalt(III) units are coordinated with pmide2−, NCS−, and CH3CO2−. The terminal units are each connected to a central cobalt(II) cation through the two oxygen atoms of pmide2− and one bridged acetate ion, giving rise to a mixed-valence trinuclear cobalt complex formulated as CoIII–CoII–CoIII. Complex 1 shows a strong antiferromagnetic interaction through the ethoxo and nitrato groups between the copper(II) ions [g = 2.070, J = –88.1 cm−1 (–61.2 K)]. However, complex 2 behaves as a paramagnetic cobalt(II) monomer, due to the diamagnetic cobalt(III) ions in the terminal units [g = 2.526, |D| = 51.8 cm−1 (36.0 K)].
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular Magnetism themed collection

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...