A rapid crosslinking injectable hydrogel for stem cell delivery, from multifunctional hyperbranched polymers via RAFT homopolymerization of PEGDA†
Abstract
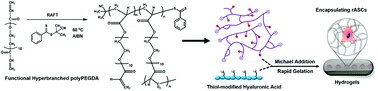
Stem cell therapies have attracted much attention for the last few decades in the field of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. The 3-dimensional (3D) microenvironment surrounding the transplanted stem cells plays an essential role that influences the cell fate and behaviors. Thus advanced functional biomaterials and extracellular matrix (ECM) replacements with adjustable chemical, mechanical and bioactive properties are requisites in this field. In this study, PEG-based hyperbranched multifunctional homopolymers were developed via RAFT homopolymerization of the divinyl monomer of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA). Due to its high degree of multi-acrylate functionality, the hyperbranched polyPEGDA can rapidly crosslink with a thiolated hyaluronic acid under physiological conditions and form an injectable hydrogel for cell delivery. In addition, by simply varying the synthesis conditions such as the reaction time and the ratio of the monomer to the chain transfer agent (CTA), the polymer molecular weight, acrylate functionality degree and the cyclized/hyperbranched polymeric architecture can be finely controlled in a one-step reaction. The gelation speed and the mechanical properties of this hydrogel can be easily adjusted by altering the crosslinking conditions. Rat adipose-derived stem cells (rASCs) were embedded into the in situ crosslinked hydrogels, and their cellular behavior such as the morphology, viability, metabolic activity and proliferation were fully evaluated. The results suggested that the hydrogel maintained good cell viability and it can be easily modified with other bioactive signals, which provide this injectable hydrogel delivery system with good potential for polymeric biomaterials and tissue regeneration applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...