Electroactive and bioactive films of random copolymers containing terthiophene, carboxyl and Schiff base functionalities in the main chain†
Abstract
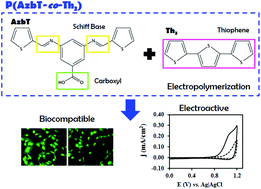
A new bis-thienyl type monomer with preformed azomethine linkages (AzbT) was chemically synthesized and, subsequently, electro-copolymerized with 2,2′ : 5′,2′′-terthiophene (Th3). AzbT : Th3 mixtures with different molar ratios (i.e. 50 : 50, 60 : 40 and 80 : 20) were considered, the resulting thin films being made of random insoluble copolymers, P(AzbT-co-Th3)s. The content of AzbT in P(AzbT-co-Th3)s was found to increase with the AzbT : Th3 molar ratio in the electropolymerization medium. Furthermore, characterization of the different copolymers suggests the existence of several concomitant processes in the reaction medium. Thus, depending on the composition of the reaction medium, AzbT worked as a co-monomer and/or as a dopant for the growing polymer chains. The morphology of the films evolved from a porous multi-level surface to a more compact and flat globular structure with increasing AzbT content. On the other hand, the electrochemical and optical properties were also influenced by the AzbT : Th3 ratio. Cytotoxicity and cell adhesion and proliferation tests, which were performed using human osteosarcoma and monkey kidney epithelial cell lines (MG-63 and Vero, respectively), revealed that P(AzbT-co-Th3) matrices can be potentially applied as bioactive substrates. This behaviour was especially relevant for the 80 : 20 copolymer, which exhibits optical and electrochemical properties in the range of polythiophene derivatives, suggesting that it is a promising functional biomaterial.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...