Dual role for alkali metal cations in enhancing the low-temperature radical polymerization of N,N-dimethylacrylamide†
Abstract
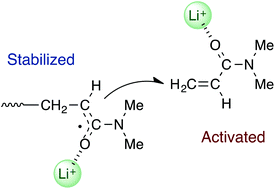
The radical polymerization of N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMAAm) has been investigated in the presence of several alkali metal salts, including lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiNTf2). The addition of an alkali metal salt led to a significant increase in the yield and molecular weight of the resulting polymer. NMR analysis of mixtures of DMAAm and LiNTf2 suggested that DMAAm was being activated by the coordination of Li+ to its C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group. Electron spin resonance analysis of the DMAAm polymerization in the presence of LiNTf2 suggested that the propagating radical was being stabilized by Li+ through a single-electron lithium bond, because a signal for the propagating radical of the acrylamide derivatives was observed for the first time in solution when LiNTf2 was added. Based on these results, we have proposed a mechanism for this polymerization, where the propagation steps occur between a lithium ion-stabilized propagating radical and a lithium ion-activated incoming monomer. Furthermore, polymers with a wide range of stereoregularities, such as isotactic, syndiotactic and heterotactic systems, were successfully prepared using this method by carefully selecting the appropriate combination of solvent and alkali metal salt.
O group. Electron spin resonance analysis of the DMAAm polymerization in the presence of LiNTf2 suggested that the propagating radical was being stabilized by Li+ through a single-electron lithium bond, because a signal for the propagating radical of the acrylamide derivatives was observed for the first time in solution when LiNTf2 was added. Based on these results, we have proposed a mechanism for this polymerization, where the propagation steps occur between a lithium ion-stabilized propagating radical and a lithium ion-activated incoming monomer. Furthermore, polymers with a wide range of stereoregularities, such as isotactic, syndiotactic and heterotactic systems, were successfully prepared using this method by carefully selecting the appropriate combination of solvent and alkali metal salt.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...