BODIPY-based macromolecular photosensitizer with cation-enhanced antibacterial activity†
Abstract
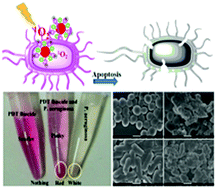
We report here an innovative study to develop a photodynamic therapy agent with high antibacterial activity to improve public health. A macromolecular photosensitizer with cation-enhanced antibacterial activity was successfully synthesized through atom transfer radical polymerization. The macromolecular photosensitizer has good stability under physiological conditions and generates a high yield of singlet oxygen (1O2) in aqueous solution. The macromolecular photosensitizer also shows antibacterial activity towards both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Bacterial growth was inhibited at concentrations of the macromolecular photosensitizer as low as 0.3 nmol mL−1; this is the lowest reported inhibitory concentration for a photodynamic therapy antibacterial agent. The macromolecular photosensitizer also showed good cytocompatibility in the dark. We investigated the mechanism of bacterial apoptosis using an absorption study at 260 nm and SEM. We concluded that 1O2 irreversibly disrupts the structure of the bacterial membrane, which ultimately leads to bacterial apoptosis. These optimized features were integrated into a single glycopolymer. These results show that the macromolecular photosensitizer has the ideal properties of a photodynamic therapy antibacterial agent. This study provides a new route with which to design photodynamic therapy antibacterial agents for biomedical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...