Synthesis of isoxazolidine-containing uridine derivatives as caprazamycin analogues†
Abstract
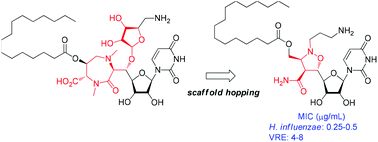
Simplification of caprazamycins, which are promising antibacterial nucleoside natural products, was conducted by scaffold-hopping of the structurally complex diazepanone moiety to the isoxazolidine scaffold. The designed isoxazolidine-containing uridine derivatives were synthesized by an intramolecular 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of alkenyl nitrone as a key step. The lactone-fused isoxazolidine intermediate was easily converted to the target compounds by sequential introduction of key substituents upon ring-opening the lactone moiety by nucleophilic substitution and electrophilic capping of the resulting primary alcohol. Several analogues exhibited good activity against H. influenzae ATCC 10211 (MIC 0.25–0.5 μg mL−1) and moderate activity against vancomycin-resistant E. faecalis SR7914 (MIC 4–8 μg mL−1).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...