A new approach for crystallization of copper(ii) oxide hollow nanostructures with superior catalytic and magnetic response†
Abstract
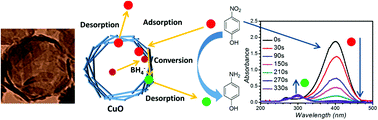
We report the synthesis of copper(II) oxide hollow nanostructures at ambient pressure and close to room temperature by applying the soft templating effect provided by the confinement of droplets in miniemulsion systems. Particle growth can be explained by considering a mechanism that involves both diffusion and reaction control. The catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol in aqueous media is used as a model reaction to prove the catalytic activity of the materials: the synthesized hollow structures show nearly 100 times higher rate constants than solid CuO microspheres. The kinetic behavior and the order of the reduction reaction change due to the increase of the surface area of the hollow structures. The synthesis also leads to modification of physical properties such as magnetism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...