Effect of surface energy on size-dependent deformation twinning of defect-free Au nanowires†
Abstract
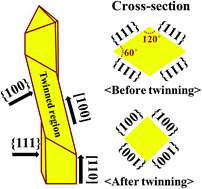
In this study, we report the size-dependent transition of deformation twinning studied using in situ SEM/TEM tensile testing of defect-free [110] Au nanowires/ribbons with controlled geometry. The critical dimension below which the ordinary plasticity transits to deformation twinning is experimentally determined to be ∼170 nm for Au nanowires with equilateral cross-sections. Nanoribbons with a fixed thickness but increased width-to-thickness ratios (9 : 1) were also studied to show that an increase in the surface energy due to the crystal re-orientation suppresses the deformation twinning. Molecular dynamics simulations confirmed that the transition from partial dislocation mediated plasticity to perfect dislocation plasticity with increase in the width-to-thickness ratio is due to the effect of the surface energy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...