Peptide flatlandia: a new-concept peptide for positioning of electroactive probes in proximity to a metal surface†
Abstract
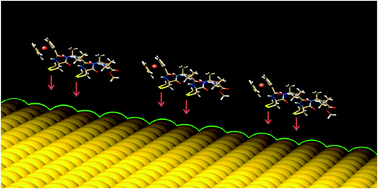
A helical hexapeptide was designed to link in a rigid parallel orientation to a gold surface. The peptide sequence of the newly synthesized compound is characterized by the presence of two 4-amino-1,2-dithiolane-4-carboxylic acid (Adt) residues (positions 1 and 4) to promote a bidentate interaction with the gold surface, two L-Ala residues (positions 2 and 5) and two-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) residues (positions 3 and 6) to favor a high population of the 310-helix conformation. Furthermore, a ferrocenoyl (Fc) probe was inserted at the N-terminus to investigate the electronic conduction properties of the peptide. X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy techniques were used to characterize the binding of the peptide to the gold surface and the morphology of the peptide layer, respectively. Several electrochemical (cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry, square wave voltammetry) techniques were applied to analyze the electrochemical activity of the Fc probe, along with the influence of the peptide 3D-structure and the peptide layer morphology on electron transfer processes.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...