Enhancing the performance of catalytic AuPt nanoparticles in nonaqueous lithium–oxygen batteries†
Abstract
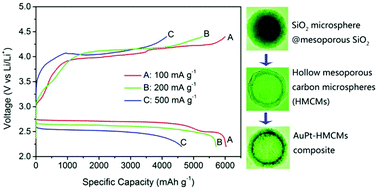
The deposition of catalytic AuPt (1 : 1) nanoparticles (NPs) into hollow mesoporous nitrogen-doped carbon microspheres (HMCMS) was found to significantly improve the effectiveness of the catalysis of oxygen reactions in nonaqueous lithium–oxygen batteries (LOBs); surpassing the performance of unsupported AuPt NPs or HMCMS in discharge and charge overpotentials (lower), specific capacity and rate performance (higher), and cycle life (longer). Specifically at a typical current density of 100 mA g−1, a LOB with the AuPt/HMCMS cathode catalyst could provide discharge and charge capacities of 6028 and 6000 mA h g−1 respectively and a charge–discharge voltage gap of only 1.27 V. The discharge capacity decreased by 5% when the current density was doubled, and by 23% when the current density was quintupled. The AuPt/HMCMS LOB could be cycled 75 times for a depth of discharge (DOD) of 1000 mA h g−1 without exceeding the charge cut-off voltage of 4.4 V. These measurements indicate that the HMCMS is an outstanding catalyst support to use for increasing the effectiveness of oxygen electrocatalysts in the LOBs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...