Single ZnO nanocactus gas sensor formed by etching of ZnO nanorod†
Abstract
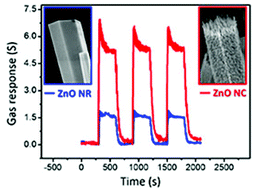
Etching of materials on the nanoscale is a challenging but necessary process in nanomaterials science. Gas sensing using a single ZnO nanocactus (NC), which was prepared by facile isotropic nanoetching of zinc oxide nanorods (NR) grown by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) using an organic photoresist (PR) by a thermochemical reaction, is reported in this work. PR consists of carboxylic acid groups (COOH) and cyclopentanone (C5H8O), which can react with zinc and oxygen atoms, respectively, on the surface of a ZnO NR. The thermochemical reaction is controllable by varying the concentration of PR and reaction time. A gas sensor was fabricated using a single NC. Gas sensing was tested using different gases such as CH4, NH3 and carbon monoxide (CO). It was estimated that the surface area of a ZnO NC in the case of 50% PR was found to increase four-fold. When compared with a single ZnO NR gas sensor, the sensitivity of a ZnO NC was found to increase four-fold. This increase in sensitivity is attributed to the increase in surface area of the ZnO NC. The formed single ZnO NC gas sensor has good stability, response and recovery time.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...