Spontaneous formation of Au–Pt alloyed nanoparticles using pure nano-counterparts as starters: a ligand and size dependent process†
Abstract
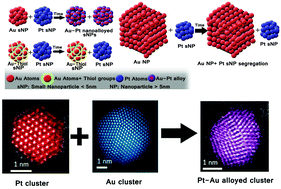
In this work we investigate the formation of PtAu monodisperse alloyed nanoparticles by ageing pure metallic Au and Pt small nanoparticles (sNPs), nanoparticle size <5 nm, under certain conditions. We demonstrate that those bimetallic entities can be obtained by controlling the size of the initial metallic sNPs separately prepared and by selecting their appropriate capping agents. The formation of this spontaneous phenomenon was studied using HR-STEM, EDS, ionic conductivity, UV-Vis spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. Depending on the type of capping agent used and the size of the initial Au sNPs, three different materials were obtained: (i) AuPt bimetallic sNPs showing a surface rich in Au atoms, (ii) segregated Au and Pt sNPs and (iii) a mixture of bimetallic nanoparticles as well as Pt sNPs and Au NPs. Surface segregation energies and the nature of the reaction environment are the driving forces to direct the distribution of atoms in the bimetallic sNPs. PtAu alloyed nanoparticles were obtained after 150 h of reaction at room temperature if a weak capping agent was used for the stabilization of the nanoparticles. It was also found that Au atoms diffuse towards Pt sNPs, producing a surface enriched in Au atoms. This study shows that even pure nanoparticles are prone to be modified by the surrounding nanoparticles to give rise to new nanomaterials if atomic diffusion is feasible.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...