The role of nanoscale defect features in enhancing the thermoelectric performance of p-type nanostructured SiGe alloys†
Abstract
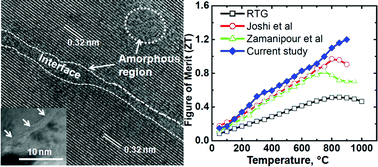
Despite SiGe being one of the most widely studied thermoelectric materials owing to its application in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG), the thermoelectric figure-of merit (ZT) of p-type SiGe is still quite low, resulting in poor device efficiencies. In the present study, we report a substantial enhancement in ZT ∼ 1.2 at 900 °C for p-type nanostructured Si80Ge20 alloys by creating several types of defect features within the Si80Ge20 nanostructured matrix in a spectrum of nano to meso-scale dimensions during its nanostructuring, by employing mechanical alloying followed by spark plasma sintering. This enhancement in ZT, which is ∼25% over the existing state-of-the-art value for a p-type nanostructured Si80Ge20 alloy, is primarily due to its ultralow thermal conductivity of ∼2.04 W m−1 K−1 at 900 °C, resulting from the scattering of low-to-high wavelength heat-carrying phonons by different types of defect features in a range of nano to meso-scale dimensions in the Si80Ge20 nanostructured matrix. These include point defects, dislocations, isolated amorphous regions, nano-scale grain boundaries and more importantly, the nano to meso-scale residual porosity distributed throughout the Si80Ge20 matrix. These nanoscale multi-dimensional defect features have been characterized by employing scanning and transmission electron microscopy and correlated with the electrical and thermal transport properties, based on which the enhancement of ZT has been discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...