One-pot laser-assisted synthesis of porous carbon with embedded magnetic cobalt nanoparticles†
Abstract
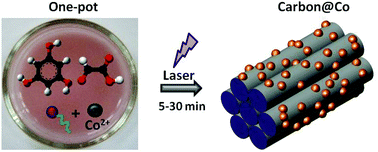
A novel one-pot laser-assisted approach is reported herein for the synthesis of ordered carbons with embedded cobalt nanoparticles. The process is based on a UV pulsed laser exposure of an ethanolic solution consisting of green carbon precursors, a structure directing agent and a cobalt salt. Very short irradiation times (5 to 30 min) are only required to polymerize and cross-link carbon precursors (i.e. phloroglucinol and glyoxylic acid) independent of a catalyst presence. The influence of three metallic salts (acetate, nitrate and chloride) on the phenolic resin and carbon characteristics (structure, texture and particle size/distribution) was systematically studied. When exposed to UV laser, the metallic salt exhibited a strong influence on the particle size and distribution in the carbon matrix rather than on the textural carbon properties. Using cobalt acetate, very small (3.5 nm) and uniformly dispersed particles were obtained by this simple, fast and green one-pot synthesis approach. An original combined 13C CP-MAS and DP-DEC solid state NMR spectroscopy analysis allowed to determine the structure of phenolic resins as well as the location of the cobalt salt in the resin. Complementarily, the 1H solid-state and relaxation NMR provided unique insights into the rigidity (cross-linking) of the phenolic resin and dispersion of the cobalt salt. The magnetic properties of cobalt nanoparticles were found to be size-dependent: large Co nanoparticles (∼50 nm) behave as bulk Co whereas small Co nanoparticles are superparamagnetic.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...