White-light induced grafting of 3-MPA on the Si(111)–H surface for catalyzing Au nanoparticles’ in situ growth†
Abstract
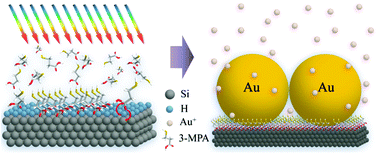
A novel, mild and effective method was designed for grafting of high-quality organic monolayers on a silicon surface to catalyze nanoparticles’ growth. By using a white-light source, 3-mercaptopropionic acid (3-MPA) molecules were attached to hydrogen-terminated Si(111) surfaces at room temperature. The attached monolayers were characterized using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to provide detailed information. The in situ growth of Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) with dimensions below 20 nm was catalyzed on a silicon surface with highly uniform and compact structure morphology. The AuNPs can grow selectively in a certain region on a patterned Si–Si3N4 chip. p-Nitrothiophenol (p-NTP) was used as the probe to evaluate the SERS enhancement of the highly uniform and compact AuNP–Si substrate. In order to better understand the white light initiation of the addition reaction of 3-MPA on the Si(111)–H surface, the mechanism was elucidated by density functional theoretical (DFT) calculations, which indicated that the formation of the Si–O bond occurred at the PEC of the first singlet excited state (S1) with a very low activation barrier about 30% of the ground state (S0) value.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...