Tunable doping of graphene nanoribbon arrays by chemical functionalization†
Abstract
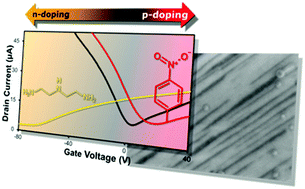
We demonstrate the controlled tuning of the electronic band structure of large-arrays of graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) by chemical functionalization. The GNR arrays are synthesized by substrate-controlled metal-assisted etching of graphene in H2 at high temperature, and functionalized with different molecules. From Raman spectroscopy and carrier transport measurements, we found that 4-nitrobenzenediazonium (4-NBD) and diethylene triamine (DETA) molecules can tune the doping level of the GNR arrays to p- and n-type, respectively. In both cases, the doping effects induced in the GNRs were found to be higher than for a pristine graphene sheet, due to the presence of a large quantity of edges. Effects of chemical doping on the Raman spectrum of sp2 carbon materials are also discussed. Our findings offer an effective way to control the electronic structure of GNRs by chemical functionalization, and are expected to facilitate the production of nanoribbon-based p–n junctions for future implementation into electronic circuits.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...