Graphdiyne–metal contacts and graphdiyne transistors†
Abstract
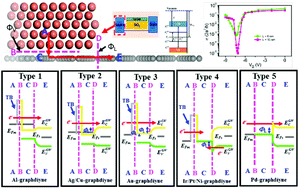
Graphdiyne was prepared on a metal surface, and the preparation of devices using it inevitably involves its contact with metals. Using density functional theory with dispersion correction, we systematically studied, for the first time, the interfacial properties of graphdiyne that is in contact with a series of metals (Al, Ag, Cu, Au, Ir, Pt, Ni, and Pd). Graphdiyne forms an n-type Ohmic or quasi-Ohmic contact with Al, Ag, and Cu, while it forms a Schottky contact with Pd, Au, Pt, Ni, and Ir (at the source/drain-channel interface), with high Schottky barrier heights of 0.21, 0.46 (n-type), 0.30, 0.41, and 0.46 (p-type) eV, respectively. A graphdiyne field effect transistor (FET) with Al electrodes was simulated using quantum transport calculations. This device exhibits an on–off ratio up to 104 and a very large on-state current of 1.3 × 104 mA mm−1 in a 10 nm channel length. Thus, a new prospect has opened up for graphdiyne in high performance nanoscale devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...