Dependency of magnetic microwave absorption on surface architecture of Co20Ni80 hierarchical structures studied by electron holography†
Abstract
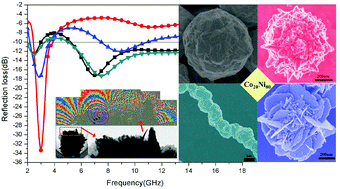
To design and fabricate rational surface architecture of individual particles is one of the key factors that affect their magnetic properties and microwave absorption capability, which is still a great challenge. Herein, a series of Co20Ni80 hierarchical structures with different surface morphologies, including flower-, urchin-, ball-, and chain-like morphologies, were obtained using structure-directing templates via a facile one-step solvothermal treatment. The microwave reflection loss (RL) of urchin-like Co20Ni80 hierarchical structures reaches as high as −33.5 dB at 3 GHz, with almost twice the RL intensity of the ball- and chain-like structures, and the absorption bandwidth (<−10 dB) is about 5.5 GHz for the flower-like morphology, indicating that the surface nanospikes and nanoflakes on the Co20Ni80 microsphere surfaces have great influences on their magnetic microwave absorption properties. Electron holography analysis reveals that the surface nanospikes and nanoflakes could generate a high density of stray magnetic flux lines and contribute a large saturation magnetization (105.62 emu g−1 for urchin-like and 96.41 emu g−1 for flower-like morphology), leading the urchin-like and flower-like Co20Ni80 to possess stronger microwave RL compared with the ball-like and chain-like Co20Ni80 alloys. The eddy-current absorption mechanism μ′′(μ′)−2(f)−1 is dominant in the frequency region above 8 GHz, implying that eddy-current loss is a vital factor for microwave RL in the high frequency range. It can be supposed from our findings that different surface morphologies of magnetic hierarchical structures might become an effective path to achieve high-performance microwave absorption for electromagnetic shielding and stealth camouflage applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...